Abstract
Google Colaboratory (Colab)*1 is Jupyter notebook environment provided by Google. Mounting Google Drive*2, user can edit files there on Colab.
This post introduces procedure to convert MP4 movie to GIF animation. Converting to GIF, MP4 is
- cropped to remove unwanted area
- resized to make outputs smaller
- thinned to drop frame rate
MoviePy or OpenCV + Pillow are used for processes above. This post also compares performance and quality of them. Although MoviePy provides better syntax, OpenCV provides massively faster performance.
Mount Google
Colab supports various way to mount Google Drive. Directory structure of Colab is as following.
🔎Colab directory structure

It should be focused that Google Drive is mounted as "/drive" under "/content". Next Linux commands also show the common fact. This is the case of mounting via Colab GUI.
!pwd !ls

In the case of mounting with Python code, "/drive" in mounted path is replaced to the designated one. Example, the next case shows mounting as "/gdrive".
!pwd
from google.colab import drive
drive.mount('./gdrive')
Preparation and assumptions
The source movie in this post (MP4 file) is the one attached at the end of the past post*3. This MP4 file is stored at the next path after mounting Google Drive via Colab GUI.
/content/drive/MyDrive/20230404/screen-20230331-142030.mp4
This time, upper half of this movie is output as GIF animation. Its assumption is
Size of movie (animation)
| width | height | |
|---|---|---|
| MP4 frame size | 1800 | 2784 |
| MP4 cropped size | 1800 | 1392 |
| GIF resized size | 640 | 495 |
They are implicitly reflected to Python program introduced later.
Convert from MP4 to GIF
Logic
Converting from MP4 to GIF, seriese of frames consist of movie are converted one by one. In this process, size of source image is smaller, converting process is faster. So, process making sources smaller has priority. This time, processes are executed in next order.
- crop
- resize
And drop frame rate finally reduces number of images converted.
OpenCV + Pillow
OpenCV (CV: Computer Vision)*4 and Pillow (PIL: Python Imaging Library) are image processing libraries for Python.
The original function "getCroppedFrames" return array of Pillow images to be converted to GIF. OpenCV is used there, and its next specification should be focused. Its default color format is BGR, and it should be converted to RGB.
Note that the default color format in OpenCV is often referred to as RGB but it is actually BGR (the bytes are reversed).
OpenCV: Color Space Conversions
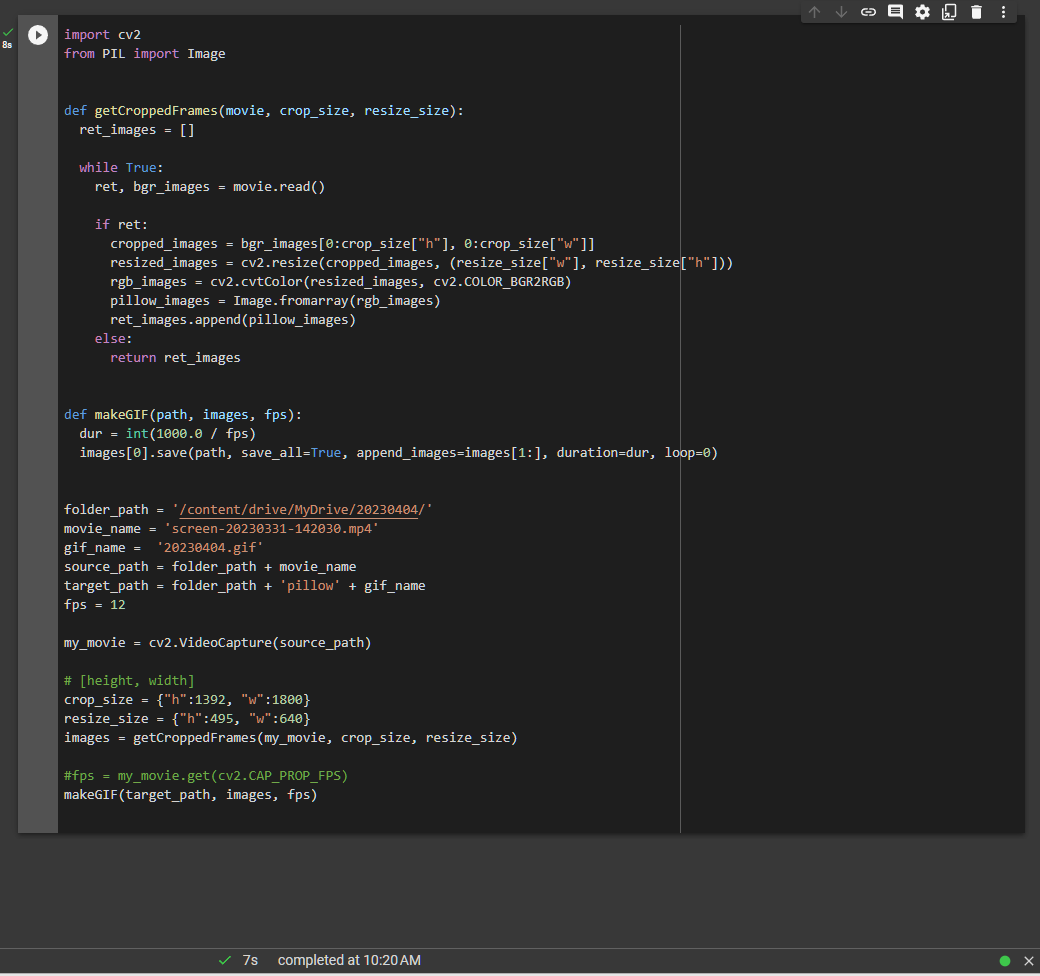
def getCroppedFrames(movie, crop_size, resize_size): ret_images = [] while True: ret, bgr_images = movie.read() if ret: cropped_images = bgr_images[0:crop_size["h"], 0:crop_size["w"]] resized_images = cv2.resize(cropped_images, (resize_size["w"], resize_size["h"])) rgb_images = cv2.cvtColor(resized_images, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) pillow_images = Image.fromarray(rgb_images) ret_images.append(pillow_images) else: return ret_images
And the other original function "makeGIF" outputs GIF file. Images to be converted are thinned with setting FPS. Image format is defined by designated path. No need to tell expected image format as parameter.
def makeGIF(path, images, fps): dur = int(1000.0 / fps) images[0].save(path, save_all=True, append_images=images[1:], duration=dur, loop=0)
Full text of source code is as following. It ends entire process around 8sec.
MoviePy
MoviePy*5 is library for video editing. Its syntax is easier to understand than OpenCV. It just can be written as programmer may expect it to be written, and it results in a program is easy to understand. Example,
input_video = VideoFileClip(source_path) cropped_video = input_video.crop(x1=0, y1=0, width=1800, height=1392) resized_video = cropped_video.resize(height=640) resized_video.write_gif(target_path_ffmpeg, fps=12, program='ffmpeg', logger='bar')
Writing in common style of OpenCV case, it is like this.
Function, getCroppedFrames
def getCroppedFrames(movie, crop_size, resize_size): cropped_movie = movie.crop(x1=0, y1=0, width=crop_size["w"], height=crop_size["h"]) resized_movie = cropped_movie.resize(height=resize_size["h"]) return resized_movie
Function, makeGIF
def makeGIF(path, movie, fps, program): movie.write_gif(path, fps=fps, program=program, logger='bar')
However, MoviePy is slow. Even if it can be written as expected, it takes 20 times longer for common processing. It takes 3 min or more to output a single GIF animation. Although it can select program as FFmpeg*6 or imageio*7 for converting to GIF, there is no big difference.
Output 2 GIF with both programs takes less than 8 min, around 3 min per a single conversion process.
Full text of source code is as following.
 |
 |
Comparison of GIF
Big difference is only syntax of program, but quality of outputs are almost no difference.
| Pillow 6.10MB |
ffmpeg 4.57MB |
imageio 4.62MB |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |