Abstract
Windows can mount ISO file, but user can't specify drive letter in advance of mounting. Its drive letter is dynamically assigned by Windows. If specific drive letter should be assigned, assigned drive letter must be changed after mounting.
This article introduces PowerShell script to mount ISO and change its drive letter.
WMI and CIM (Common Information MODEL)
WMI (Windows Management Instrumentation) and WMIC utility (WMI Command-line utility) are essential tools for Windows infrastructure management, though they are deprecated after 21H1 of Windows 10 and Windows Server (semi-annual channel).
The WMI command-line (WMIC) utility is deprecated as of Windows 10, version 21H1, and as of the 21H1 semi-annual channel release of Windows Server.
Although it is provided as an optional feature in Windows 11, it is also not recommended in Windows 11 as well, because Microsoft ends its development.
Settings > Apps > Optional features
Instead, Microsoft recommends to use CIM (Common Information Model) Cmdlet. CIM*1 is defined by DMTF (Distributed Management Task Force), and WS-Man (Web Services-Management protocol) is its protocol.
Microsoft is focusing mixed environment consist of Windows and non-Windows including public/private cloud, and supports CIM for their efficient management. At this point, WMI works as
| WMI | Windows CIM server |
| WinRM | Windows WS-Man protocol |
Even WMIC is deprecated, WMI is not not deprecated together. Although CIM works commonly for Windows and non-Windows, it needs to call WMI for Windows management. Keys are,
- WMI Cmdlet is not used
- CIM Cmdlet is used instead
- No change to call WMI
Perhaps because of heavy use of business scene, CIM Cmdlet seems to be designed carefully and considerably especially for migration from WMI. With a few exception, basic migration tactics is replacement from "Wmi" to "Cim" in scripts. Exceptions are treatment not to bring bad expression style in WMI, it is rather improvement.
You will also notice that in some places we have broken this rule – and script using WMI cmdlet can’t be simply changed to CIM cmdlet by changing the cmdlet name. e.g.
You will also notice that in some places we have broken this rule – and script using WMI cmdlet can’t be simply changed to CIM cmdlet by changing the cmdlet name. e.g.
Revisit the basics
| device disk drive |
hardware virtual hardware their abstraction |
office floor |
| partition | border that separates disk space | partition board |
| volume | partitioned disk space | room |
| drive letter | pointer to partition or volume | room number |
Concept of a device and disk is almost snynonymous. Although they are used synonymously as HDD, optical drive, etc, they refer to an abstract equipment regardless of physical or logical. This is because there are cased where multiple physical HDD are logically formed into a single drive as RAID, and there are cases where is it a virtual disk file that is mounted as a storage of virtual server. Here, "disk" is all-inclusive term of them.
Disk space is separated according to the needs. A separation (border) of partitioned space is called "partition" It refers only border, doesn't include space. Partitioned space is called "volume".
And drive letter is assigned to partition or volume. It works as mount point of partition or assigned disk space.
If disk is an office floor, partition is a partition board, volume is a room, and drive letter is room number.
In PowerShell, drive letter is operated at the level of partition. And a drive mounting ISO file has only volume without partition.
Mounting ISO file
Note
Scripts introduced in this post required administration privileges. If they runs on PowerShell, VSCode, Terminal, etc, these application must be "Run as administrator"

Approach - Bad pattern
Following process is normal approach, but it doesn't work for a drive mounting ISO file. There are no partition.
- Mount ISO file
- Get its volume
- Get its partition
- Change drive letter of the partition
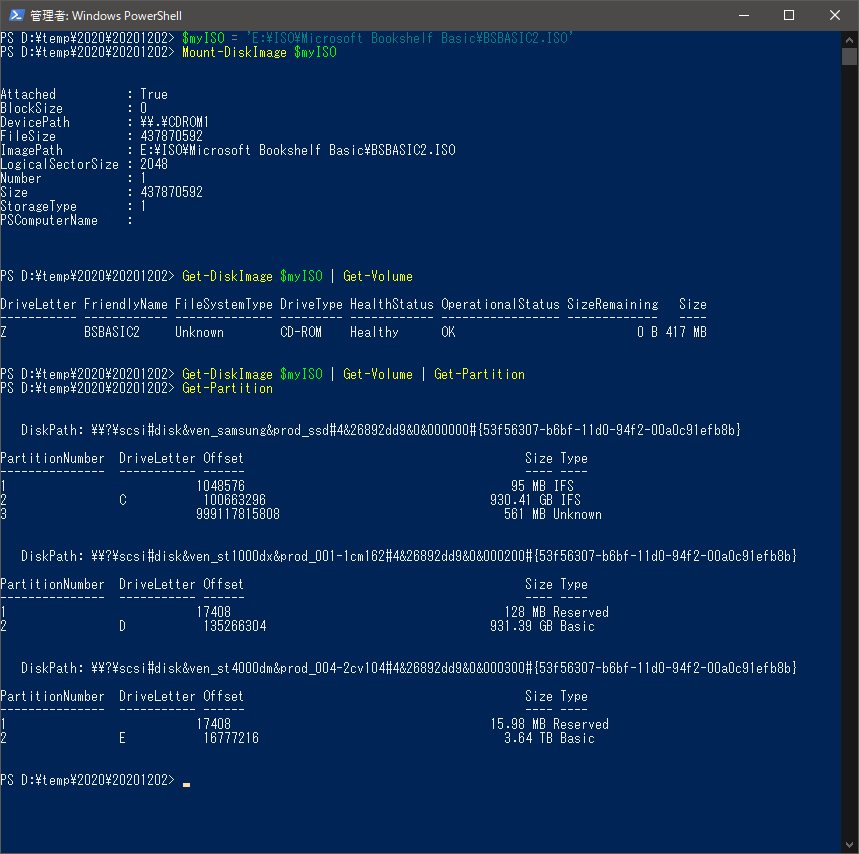
ISO is mounted at Z drive. Although a volume is referable, partition is not. Z drive is not listed as partitions. As conclusion, changing a drive letter with "Set-Partition" doesn't work here.
Approach - Good pattern
To operate a drive letter at the volume level, available options are
- diskpart
- mountvol
- WMI object
Following process is the case with WMI object, and this process works.
- Mount ISO file
- Get its volume
- Identify assigned drive letter
- Change a drive letter through WMI object
Explain codes in order. First, define the absolute path of the ISO file in myISO and mount it.
$myISO = 'E:\ISO\Microsoft Bookshelf Basic\BSBASIC2.ISO' mount-diskimage $myISO
Get the volume of ISO file, and identify assigned drive letter.
In PowerShell, drive letter is expressed in a single character as "X" and "Y", but WMI handles it with ":" as "X:". Be careful.
And define new drive letter.
$vol = Get-DiskImage $myISO | Get-Volume $old_drv = $vol.DriveLetter + ':' $new_drv = 'X:'
Then, get the list of volume information as a WMI object.
From the acquired volume information, identify the volume with assigned drive letter, and instantiate it with the drive letter newly defined.
This series of flows is executed in a single line via pipe.
Get-WmiObject -Class Win32_Volume | Where-Object {$_.DriveLetter -eq $old_drv} | Set-WmiInstance -Arguments @{DriveLetter=$new_drv}

As its result, the drive letter is changed to "X".
If these process should be executed as regular routine, same them as a script file and register in Task Scheduler.